Principle and selection of solid mixer (1)
Solid mixing technology is mainly used in pharmaceutical, food, pesticide, chemical and other industrial production, the application is extremely wide. In the pharmaceutical production, for the preparation of raw materials or product standardization and homogenization, the mixer is an indispensable device.
1. The role of mixing
Mixing refers to the two or more components in the dry state or the presence of a small amount of fluid, under the action of external forces to reduce their inhomogeneity, mutual dispersion and achieve a homogeneous state of process operations, the so-called two or more components, can be different substances, but also the same substance and have different physical properties: such as different water content, different particle diameter, different colors, etc.
2. Mixing mechanism
2.1 Convective mixing
As a result of the rotational movement of the mixer shell, impeller or spiral belt and other internal components of the machine, prompting the particle group to move substantially in position, thus forming a circular flow, that is, a lot of material particles in a mass from one place in the mixing chamber to another, and another place for the material to move in the opposite direction, the two groups of materials in the convection of mutual penetration of displacement and mixing.
2.2 Shear mixing
Mixed materials in the work of the role of the parts of each other to form a number of relative sliding shear surface and mixing occurs, which is due to the speed distribution within the particle group, the particles will certainly slide or collide with each other. For example, the mixing impeller tip and the casing wall, the gap between the bottom surface is small, the compressive force on the powder condensation group, shear force, so that the powder group fragmentation and other reasons caused by the mixing.
2.3 Diffusion mixing
The local mixing caused by two adjacent particles changing position with each other. In this case, the mixture moves around as a single particle unit, and this movement is similar to the diffusion process of fluid molecules, which is disordered.
Generally speaking, in all kinds of mixers, the above three mechanisms exist at the same time, the only difference is that according to the physical properties of the materials handled and the form of the mixer, the degree of influence on the mixing operation can be different.
3. Mixer types
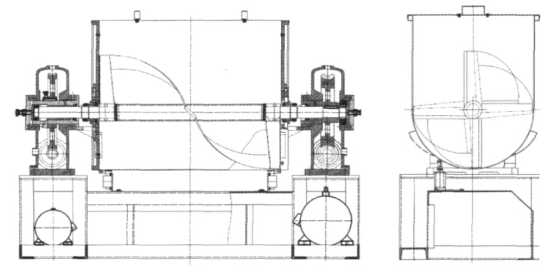
3.1 Container rotary type
Advantages: The container transformation is characterized by continuous rotation of the material storage tank of the mixer, which leads to uniform mixing of materials in the tank. This kind of mixer has a simple structure, slow mixing speed, high final mixing degree and easy cleaning inside the mixer.
Apply to: It is suitable for the mixing of powder with a small difference in physical property and good fluidity, and also for the mixing of powder particles with abrasion.
Structure diagram:
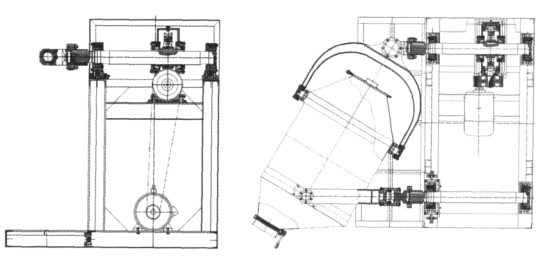
3.2 Mechanical agitation type
Apply to: The storage tank of the mechanical stirring mixer is fixed, and the rotating of the mixer installed in the tank is used to achieve the purpose of mixing materials. It can handle the powder with strong adhesion and agglutination, wet powder and paste material, and is also suitable for the mixing of the material system with a big difference in physical properties.
Advantages: This kind of mixer has a high filling rate, small operating area, small occupying space and easy operation. Due to its closed design and jacket installation, it can work at very warm and atmospheric pressure, and can also be used for reaction, granulation, drying, coating and other combined operations.
Disadvantages: The maintenance and cleaning of the machine are difficult, the incidence of failure is high, and the container and mixer will partially consolidate the powder.
Structure diagram:
3.3 Airflow type
Air flow type is an operation method that uses the upward flow or jet effect of airflow to achieve uniform mixing of powders. It is suitable for mixing between powders with good fluidity and small differences in physical properties. When intermittent operation, the filling rate can reach about 70%, and the mixing tank can be used as a storage tank.




