H2/Coal Reduction: Mineral Processing & Smelting Revolution
Against the backdrop of global climate change, China is actively seeking ways to reduce carbon dioxide emissions in order to achieve the strategic goals of carbon neutrality and carbon compliance. In this context, the application of H2/coal based reduction technology in the field of refractory mineral processing and smelting is leading a new technological revolution.
Technical background and policy support
In recent years, senior leaders in China have attached great importance to the exploration and development of energy and mineral resources. General Secretary Xi Jinping emphasized that achieving carbon peak and carbon neutrality is a broad and profound systemic change in the economy and society, which needs to be incorporated into the overall layout of ecological civilization construction. Minister of Natural Resources Wang Guanghua also proposed three directions to strengthen the exploration and development of important energy and mineral resources, including launching a new round of breakthrough strategic actions for mineral exploration, improving relevant policies to attract social capital to invest in mineral development, and strengthening technological support for mineral exploration.
Comparison between traditional and special metallurgical processes
The traditional metallurgical process involves beneficiation before smelting, but for complex and difficult beneficiation, this process has problems such as high beneficiation difficulty and low utilization of mineral resources. In contrast, powder metallurgy, as a special metallurgical technology, can reduce iron oxide to metallic iron at lower temperatures, and then remove impurities through processes such as melting and refining, ultimately obtaining high-purity molten steel. This technology not only improves the utilization rate of ore, but also reduces energy consumption and production costs.
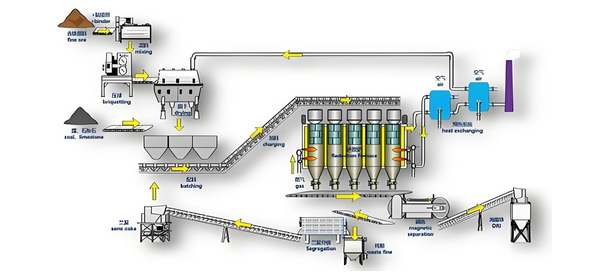
Process route of H2 reduction method
The H2 reduction method is an important process route in powder metallurgy technology. This process grinds iron concentrate powder or high phosphorus oolitic hematite block ore into powder ore, adds additives and pellet binders to mix and press the pellets, and then enters the non muffle H2 reduction furnace for reduction. The reduced sponge iron blocks are preheated with gas and continuously melted in a modified intermediate frequency furnace to obtain metal iron blocks that meet the requirements of steelmaking. This process not only occupies a small area and is fully mechanized for continuous production, but also significantly reduces operating and production costs.
Coal based vertical furnace process route
In addition to the H2 reduction method, the coal based vertical furnace method is also an important process route in powder metallurgy technology. This process involves mixing iron concentrate powder with additives and pellet binders to form pellets, which are then mixed with reducing agents and sent into a coal based vertical furnace for reduction. The restored sponge iron block is also preheated with gas and continuously melted in a modified electric furnace to obtain a metallic iron block. Compared with traditional blast furnace technology, coal based vertical furnace method has significant advantages in resource applicability, pollutant emissions, etc., and is an important direction for the development of low-carbon ironmaking new technology.
Innovation points and core control points
The innovation of H2/coal based reduction technology lies in the use of a short process steelmaking process route that combines powder metallurgy and high phosphorus oolitic hematite comprehensive metallurgy, forming a new, complete and systematic high-quality short process metallurgical process for green, low C, low S, low P, low impurity, and high-purity molten steel. The core control points of this process lie in the control of desulfurization, dephosphorization, and element reduction. By precisely controlling the process parameters and metallization rate during the reduction process, it is possible to achieve effective utilization of refractory minerals such as high phosphorus oolitic hematite and vanadium titanium magnetite, while significantly reducing energy consumption and production costs.
Here is the translation of the given information into an English table:
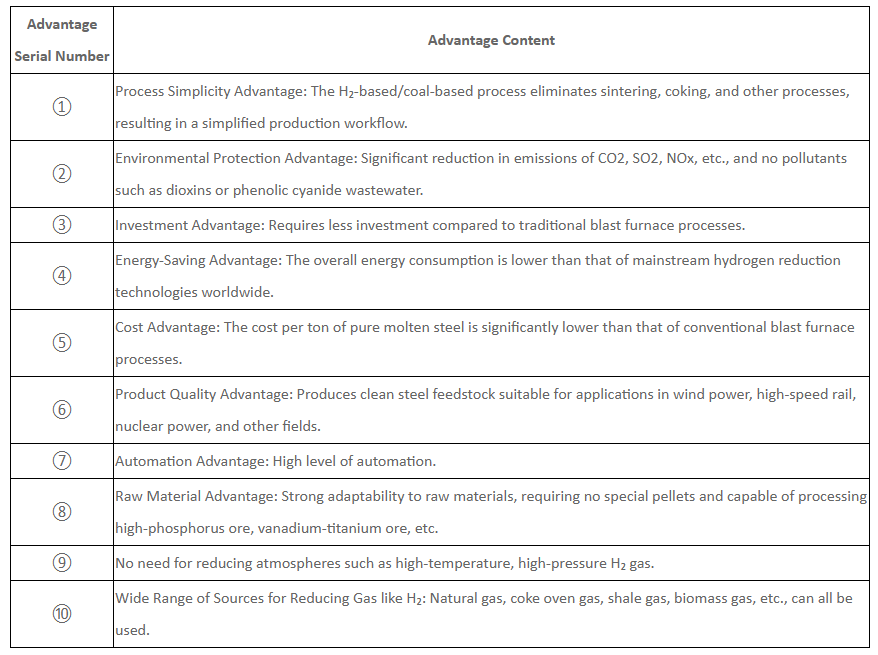
Application prospects and significance
The application prospects of H2/coal based reduction technology are broad, which is not only suitable for the comprehensive utilization of difficult to process minerals such as high phosphorus oolitic hematite and vanadium titanium magnetite, but also provides strong support for the green transformation and sustainable development of the steel metallurgy industry. The successful application of this technology will help improve the utilization rate of mineral resources and the quality level of steel products in China, while reducing energy consumption and production costs, and promoting the transformation and upgrading of the steel metallurgy industry and high-quality development.




